Tanga Region is one of the 30 regions of Tanzania. Its Regional Headquarters is in Tanga. Tanga region is situated at the extreme north-east corner of Tanzania between 40 and 60 degrees below the Equator and 370-39010′ degrees East of the Greenwich meridian. The region occupies an area of 27,347sq kms, being only 3% of total area of the country.
The region is bordered to the north by Kenya and Kilimanjaro Region, to the East by the Indian Ocean, to the South by Pwani and Morogoro regions, and to the West by Manyara Region.
The Region was previously known as Tanga Province, which, however, included the Same and Mwanga districts which are at present in Kilimanjaro Region.
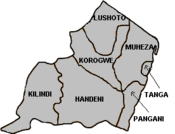
Administratively, Tanga Region is divided into seven districts: Tanga, Muheza, Korogwe, Lushoto, Handeni, Pangani and kilindi. The region has a total of 37 divisions. 136 wards and 557 villages. The Regional Administrative Secretary is the Chief Executive in the region assisted by District Executive Directors at district level and other functional officers; while the Regional Commissioner is the administrative overseer and represents the President in the region.
The region has a land area of 27,348sq kms, of which total area available for agricultural activities is 17,000sq kms only.
Population
According to the 2002 Tanzania National Census, the region has a population of 1,642,015 people.
Tribes
The tribes include Wazigua, Wabondei, Wasambaa, Wadingo, Segeju the migrated tribes to the Region are the Pare, Wataita, Wambugu and Wanago.
Economy
In spite of the tremendous resources and other potentials that Tanga region is endowed with as well as the good infrastructure it possess, the region is underdeveloped. The agricultural sector faces a number of problems including inadequate utilization of fertilizers and other agricultural inputs. People practice shifting cultivation and burning of open spaces and use very poor agricultural technology due to low level of education among the farmers.
 Despite the problems and challenges Tanga region faces, given its tremendous potentials, the region is seen by most people as a strategic one that can be explored to stimulate Tanzania and East African development.
Despite the problems and challenges Tanga region faces, given its tremendous potentials, the region is seen by most people as a strategic one that can be explored to stimulate Tanzania and East African development.
It is cited that the huge arable land, varieties of minerals, different types of tourist attractions and a good infrastructure especially the Tanga port, have made the region a gateway to East Africa.
The economic potential of Tanga region is in fishing, agriculture, tourism, mining industry and commerce.
The region has large, medium and small size industries. The activities of these industries range from food processing, beverages, textiles and clothing, processing of crops, particularly sisal and tea, timber and wood products, pulp and paper production. Other includes building materials production, steel and iron plants.
There are tourist attractions in Tanga which have chains of wildlife national parks with a wide variety of animals. Other tourist attractions in Tanga include old stone buildings. Amboni valleys, Amani National Reserve, Lushoto forests and coastal beaches.
There are a number of good hotels to accommodate tourists in the region. It can be deduced that there are plenty of investment opportunities in all sectors of the economy especially agricultural food crops which grow in Tanga, including maize, cassava, bananas, fruits and vegetables.
Cash crops grown in the regions are sisal, cashew nuts, coffee, tea, cotton coconuts, cardamom and tobacco.

